What is Rhamnan?
In Japan, there is a culture of eating seaweeds, which contain polysaccharides. Seaweeds have traditionally been used in the Japanese diet . Monostroma nitidum (aosa seaweed) is a widely consumed seaweed in Japan. It is commonly known as “aosa”, and is generally sold in the name “aosa seaweed/aonori” or simply “aosa.”
Aquaculture of M. nitidum is thriving in the Ise-Shima region of Mie Prefecture, contributing to approximately 60% of the country’s total yield . With this region being one of the most environmentally suitable locations for the aquaculture of M. nitidum, a group led by Professor Kida at Mie university’s seaweed laboratory (now the Faculty of Fishery Science, Department of Biology) developed a method of farming of this seaweed. With a history of practical use and adoption practices centered around the prefecture’s fishery research centers, Mie Prefecture has become the central region for the production of this seaweed.
Although not well known, M. nitidum enhances the taste of different foods such as miso soup, vinegar, soy sauce based preparations. However, recently, major wholesale distributors are stocking M. nitidum because of its increasing demand.
M. nitidum is not only a delicious seaweed, but also contains many components that are good for health. One of these components is rhamnan sulfate, which is a polyrhamnose saccharide that contains rhamnose and sulfated rhamnose. M. nitidum comprises approximately 50% rhamnan sulfate.
A substance similar to rhamnan sulfate is fucoidan. Fucoidan is a viscous polysaccharide present in seaweeds such as konbu and wakame. It is a polysaccharide that contains fucose, and constitutes its own sulfate group; therefore, it is categorized as a polysaccharide similar to rhamnan sulfate. Fucoidan is reported to have anti-tumor and anticoagulant effects, along with many other bioregulatory effects.
Rhamnan sulfate is considered a dietary fiber for living organisms, as it is not digested by digestive enzymes. Rhamnan sulfate is expected to have many positive functions for living creatures, since it is a polysaccharide similar to fucoidan. In recent years, research on the beneficiary effects of rhamnan sulfate has advanced and it is confirmed that rhamnan sulfate has many bioregulatory effects.
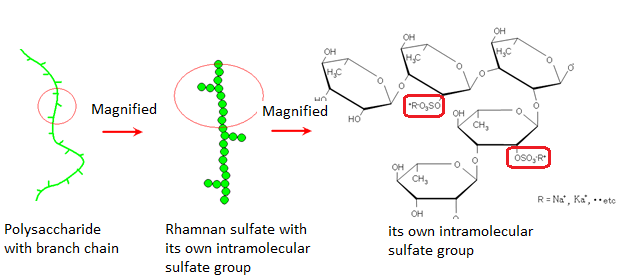
Structure of Rhamnan Sulfate
- Sulfate group with a bonded structure, with a linear chain within a branched chain.
- Sulfated polysaccharides with a molecular weight between 10,000-999,000.
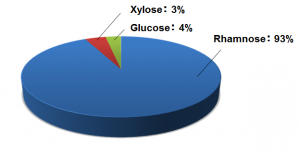
Sugar composition of rhamnan sulfate
Rhamnan sulfate contains over 90% rhamnose, a type of saccharide.